https://en.people.cn/n3/2025/0530/c98649-20322033.html
A platform on real-scene 3D modeling of the city of Qingdao was launched in March 2021 under the leadership of the Qingdao Institute of Survey and Mapping
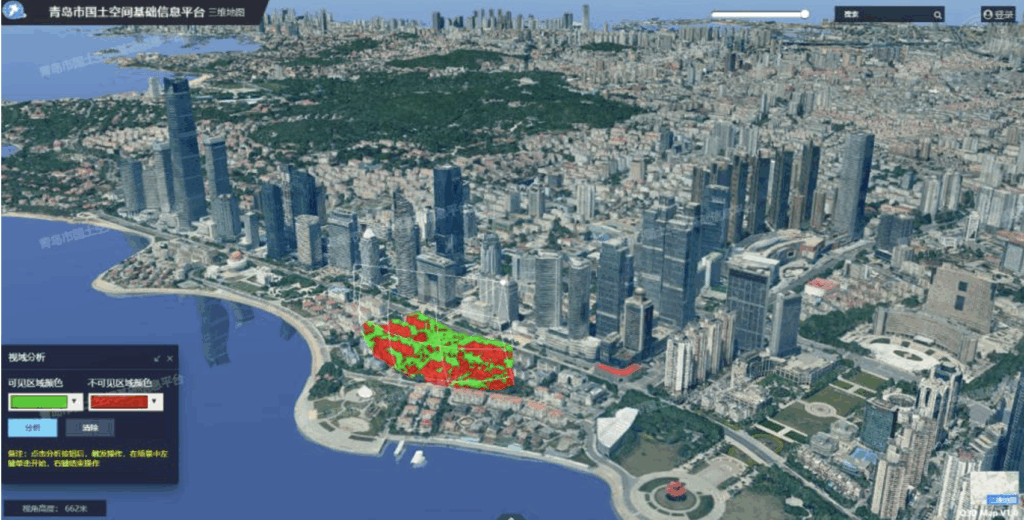
Qingdao’s varied topography – marked by hilly terrain and dramatic elevation changes – necessitated the use of oblique aerial imaging to capture raw imagery and build an accurate 3D model. The project team deployed manned fixed-wing aircraft equipped with 150-megapixel, five-lens oblique aerial cameras. The aerial survey covered the entire urban area, achieving a ground resolution of 15 centimeters and maintaining more than 70 percent image overlap to maximize accuracy.
In March 2022, following expert review, the project was officially launched for citywide application. Today, the platform covers Qingdao’s entire land area – 11,000 square kilometers – as well as 800 kilometers of coastline, 49 bays, and seven inhabited islands.
The 3D simulation platform has been shared with over 60 municipal departments. It supports more than 100 key functions, including disaster prevention and mitigation, urban planning, social governance, and urban renewal. The platform also underpins over 70 digital government service applications and records nearly 100 million uses annually. As an example, at the bureau’s headquarters, staff members examined two versions of a digital model for a former mining site in Qingdao’s West Coast New Area. The comparison revealed tangible signs of ecological restoration – more vegetation and a gentler slope. Qingdao is home to 898 legacy mine sites. In the past, inspecting these sites required a full month of on-the-ground efforts. Now, with the help of the 3D model, the same work takes just five days.
Since 2023, the city has carried out annual temporal updates to the city-scale 3D simulation platform, enabling it to track urban changes with precision and support data-driven lysis and evidence-based planning.