https://www.cell.com/the-innovation/fulltext/S2666-6758(24)00125-5
https://www.cas.cn/syky/202408/t20240823_5029609.shtml
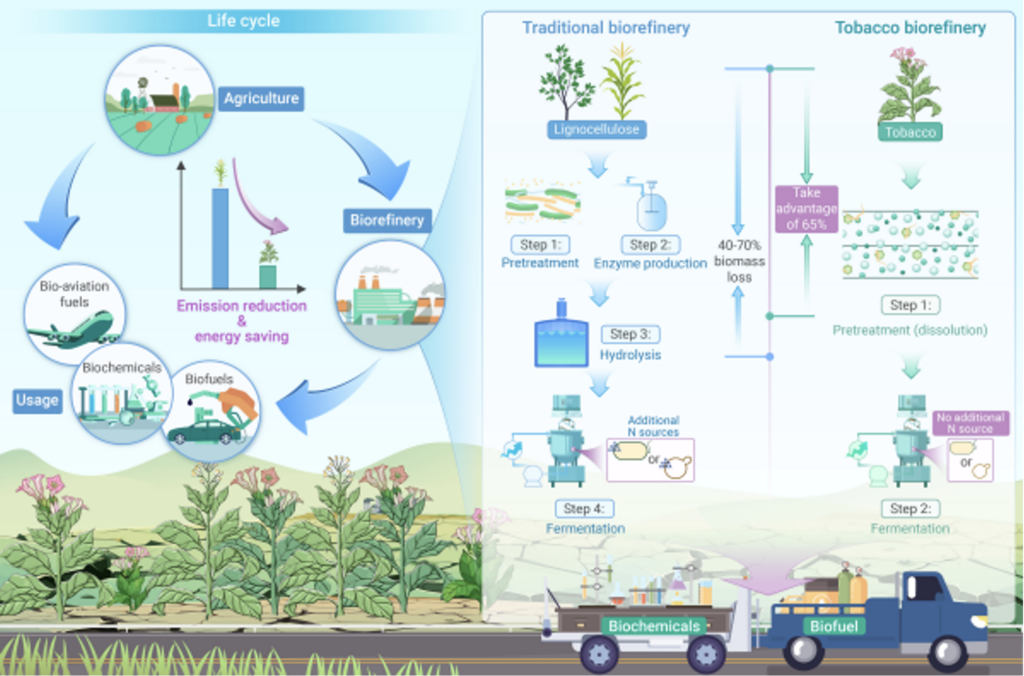
A research team led by Zhang Haibo and Fu Chunxiang, researchers at the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Wang Qian, a researcher at the Tobacco Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Sang Yup Lee, a professor at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology, found that tobacco can be used as an energy crop to achieve efficient and low-carbon utilization of biomass energy and help the sustainable development of biorefining. Compared with traditional biomass raw materials, tobacco leaves have the characteristics of high water solubility, high nitrogen content and low lignocellulose content. After the tobacco leaves are sterilized with water, a liquid with comprehensive and rich nutrition and strong biocompatibility can be obtained. This liquid can be used as a culture medium directly for the cultivation of prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and can also be directly used for the biosynthesis of bio-based fuels and bio-based chemicals.
In addition, tobacco is a field crop with strong stress resistance, salt and alkali tolerance, large biomass, and easy genetic modification, and can adapt well to the environment of marginal land. Planting tobacco on marginal land is expected to produce at least 1.17×1010 Mg of tobacco leaves per year, and theoretically 2.21×1012 L of ethanol. The results of life cycle assessment show that compared with corn straw ethanol, tobacco ethanol has reduced carbon emissions by about 27% and energy consumption by about 26%. Among them, carbon emissions in the bioconversion stage have been reduced by about 76% and energy consumption has been reduced by about 81%. This study directly sterilized tobacco leaves as a culture medium, omitted two steps, improved the biorefining route, reduced carbon footprint, and laid the foundation for achieving carbon negative emissions from bioenergy utilization.