http://english.qibebt.cas.cn/ne/rp/202502/t20250218_902019.html
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030438942500353X?via%3Dihub
https://enviromicro-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1751-7915.13580
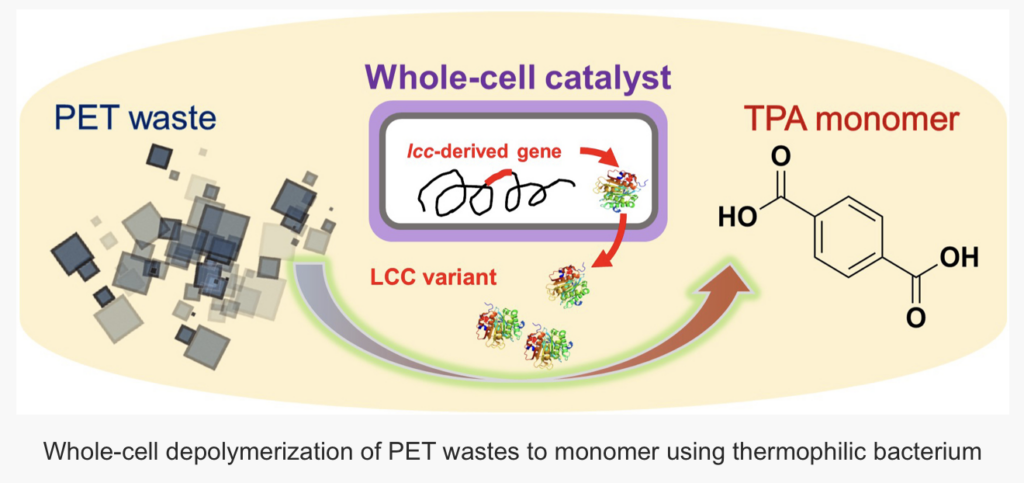
A research team from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Nanjing Tech University and Greifswald University, has introduced an innovative solution for the depolymerization of polyethylene terephthalate (PET). This solution utilizes an engineered whole-cell biocatalyst based on the thermophilic bacterium Clostridium thermocellum.
This study builds on prior work, where the research team first demonstrated the concept of whole-cell catalytic PET depolymerization. In that study, the genetically engineered C. thermocellum expressed leaf compost cutinase (LCC) via a plasmid for high-temperature PET depolymerization.
In this study, the researchers integrated LCC directly into the chromosome of C. thermocellum, ensuring stable enzyme expression. They further enhanced the system by introducing LCC variants and co-expressing hydrophobic modules.
By optimizing reaction conditions and controlling pH, the researchers achieved a significant improvement in PET depolymerization efficiency with minimal accumulation of the intermediate product mono(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (MHET).
When tested with pretreated PET bottle particles, about 97% of the added PET was converted into terephthalic acid (TPA), a key monomer used in producing new plastics or high-value chemicals. This high level of performance positions the system as a promising green solution for PET recycling.
Additionally, C. thermocellum is naturally capable of degrading cellulose, making it a potential candidate for directly processing mixed textile waste that contains cotton fibers and PET.