https://www.cas.cn/syky/202301/t20230119_4872848.shtml
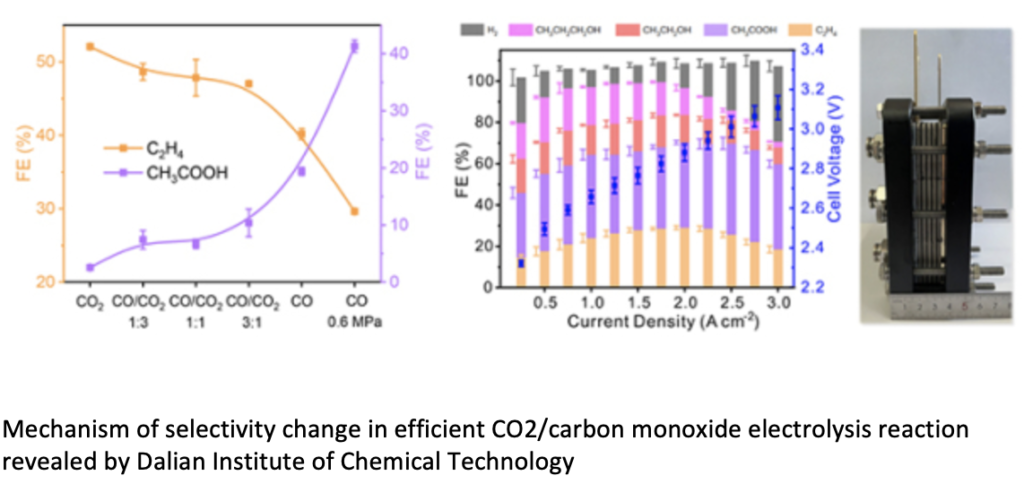
The iron and steel industry emits a large amount of carbon dioxide/carbon monoxide mixed waste gas. By applying carbon dioxide/carbon monoxide electrocatalytic reduction in an alkaline membrane electrolyzer with a copper oxide cathode, different products could be prepared. With the increase of carbon monoxide pressure in the feed gas, the main product of electrolysis gradually changed from ethylene to acetic acid, and the current density increased significantly. Under the condition of 0.6 MPa CO, the faradaic efficiency of acetate is 48%, and the total current density reaches 3 A cm-2. Mechanistic studies indicated that low CO coverage favored the formation of ethylene, and high CO coverage and high local pH favored the formation of acetic acid. Under optimized electrolysis conditions, the Faradaic efficiency and partial current density of multi-carbon products reached 90.0% and 3.1 A cm-2, respectively, corresponding to 100.0% carbon selectivity and 75.0% yield. To further verify the feasibility of the electrolysis process, the team assembled four 100 cm2 alkaline membrane stacks with a maximum electrolysis power of 2.85 kW. When the total current was 150 A, the ethylene generation rate was 457.5 mL min-1 ; When the total current was 250 A, the generation rate of acetic acid was 2.97 g min-1.