https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-54800-2
http://en.people.cn/n3/2024/1226/c90000-20258979.html
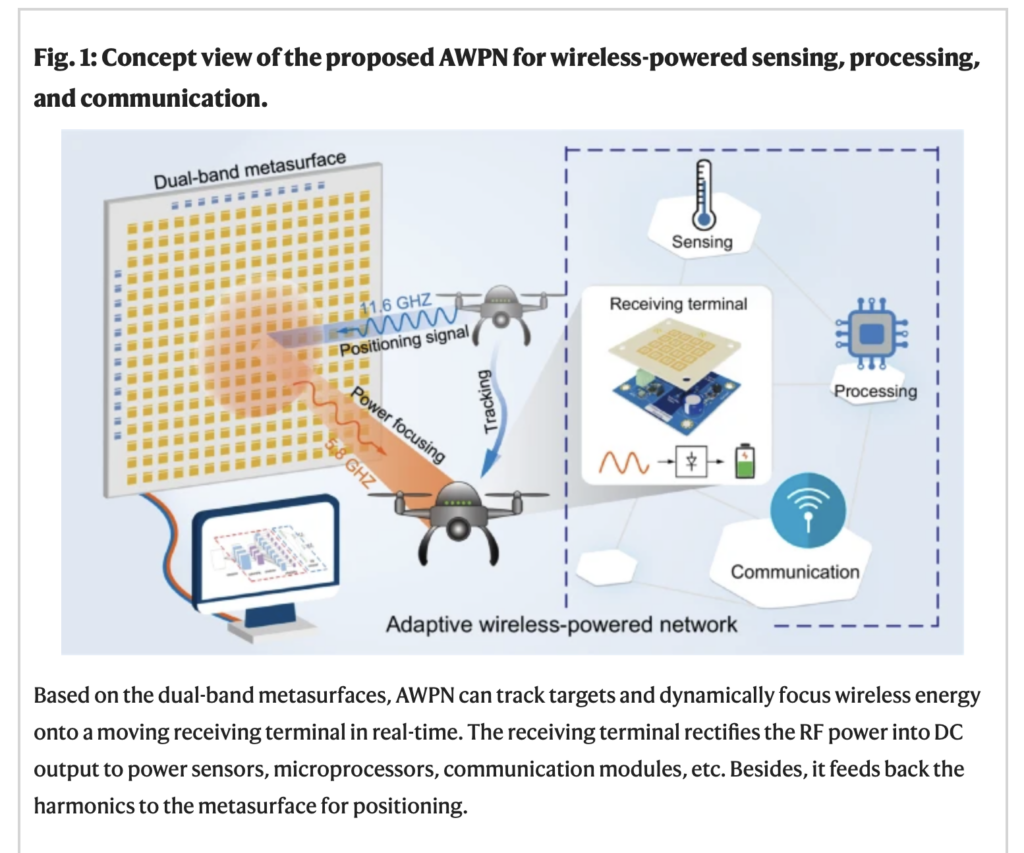
A research team around LI Long of Xdian University has achieved a significant breakthrough in wireless energy transfer and positioning which might be applied to the Internet of Things, smart homes, drones, and wearables.
Traditional wireless charging relies on close proximity and high-power electromagnetic induction, which is limited by spatial, environmental and equipment constraints. The team has successfully developed a prototype system based on dual-frequency metasurfaces for wireless energy transfer, sensing, positioning and communication. This system enables adaptive tracking of wireless energy transfer, potentially making dynamic wireless charging more efficient. The technology can adjust the transmission parameters of electromagnetic waves, optimizing wireless energy transfer efficiency in real time based on environmental changes and device requirements. Compared to traditional wireless charging methods, the new technology has significant advantages. It supports efficient non-contact wireless charging for multiple terminal devices in motion, such as drones and smart robots, providing stable and efficient power supply and thus overcoming the limitations of traditional wireless charging technology.