https://www.cas.cn/syky/202412/t20241206_5041382.shtml
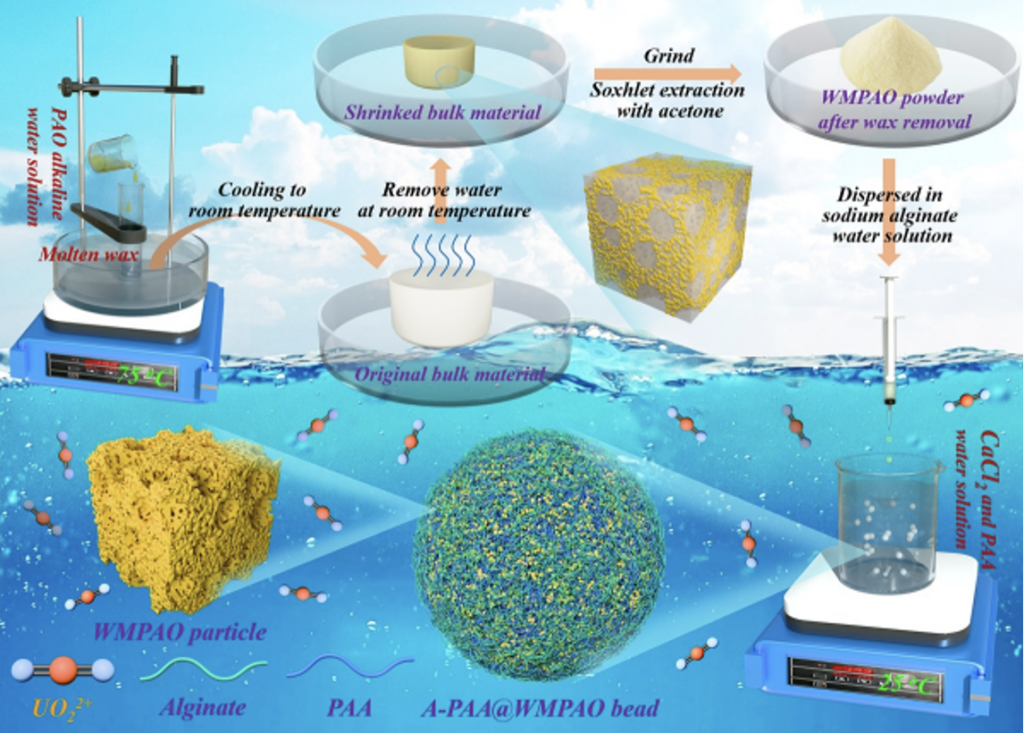
The team of Chen Jiping at the CAS Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, has used a wax casting method and a “phase conversion” process to prepare polyamidoximine (WMPAO) hydrogel particles with a macroporous structure, and coated WMPAO into alginate-polyacrylic acid (A-PAA) spheres to prepare A-PAA@WMPAO composite sphere materials. The composite sphere material can be used for the enrichment and separation of uranyl ions in seawater.
This study used the co-melting of PAO alkaline aqueous solution and wax to prepare wax-cast macroporous PAO (WMPAO) hydrogel; after cooling to room temperature, the water in the obtained white solidified block material was removed by natural volatilization to obtain a shrunken light yellow hard block material; the obtained block material was ground into fine particles and dewaxed, and the obtained WMPAO hydrogel particles had obvious cheese-like morphology and abundant macropores. In order to facilitate the extraction of uranium from seawater and material recovery, the prepared WMPAO hydrogel particles were coated into A-PAA balls. The study found that the A-PAA@WMPAO composite ball has high adsorption capacity, good mechanical strength and reusability, as well as ideal affinity and selectivity for uranyl ions. The extraction efficiency of A-PAA@WMPAO balls for uranium in spiked real seawater is 95.9 to 99.5%, and the uranium adsorption capacity obtained for 10 L of real seawater is 4.79 mg/g.