http://j.people.com.cn/n3/2025/0207/c517455-20273369.html
https://www.recordchina.co.jp/b948125-s6-c20-d0189.html
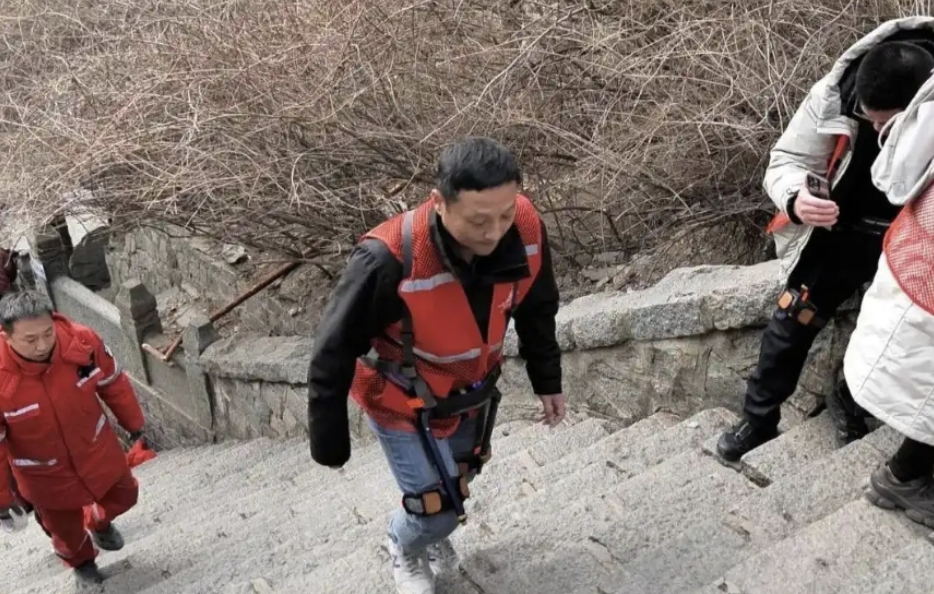
During the Chinese New Year holiday, a mountain climbing support robot jointly developed by Taishan Wenlun Group and Shenzhen Kenqi Technology Co. was test-introduced in the Taishan Scenic Area. Guangming reported.
According to Taishan Wenlun Group, the mountain climbing support robot can be used in a wide range of areas in daily life and work, such as mountain climbing, fitness, running, walking, and climbing up and down stairs. It weighs just 1.8 kilograms and is ergonomically designed with power, electronics and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. It can sense every movement of the lower limbs and provide support at the right time.
According to the group, it can operate continuously for more than five hours. The product is currently in the trial operation phase, and the company plans to launch 200 units on the market in early March.