https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2024.116784
https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/tech/202409/t20240929_690937.shtml
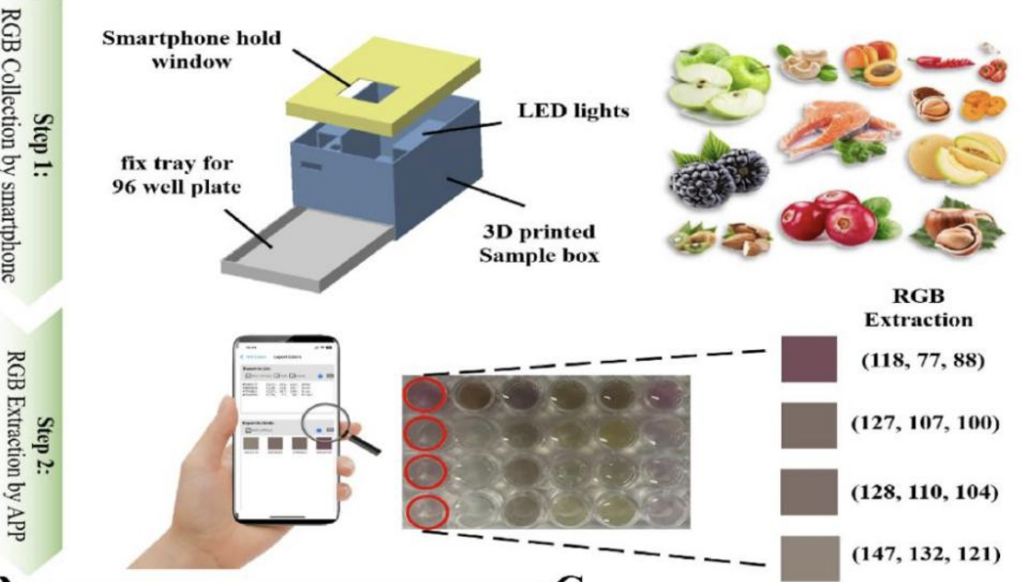
Two scientists at the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei have developed a sensor system for detecting resveratrol, tea polyphenols, chlorogenic acid, rutin and vanillin in food. Dyes are produced by oxidizing these substances on copper nanozymes with laccase activity in the presence of 4-aminoantipyrine. If adenine, guanine, inosine or cytosine are used to produce the copper nanozymes in low-temperature plasma, the dye patterns differ and, with the help of a colorimetric code, allow a quantitative determination of the ingredients in the concentration range of 1.5 – 150 µg/ml on the smartphone.