https://www.cas.cn/syky/202406/t20240603_5016507.shtml
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.orglett.4c01079
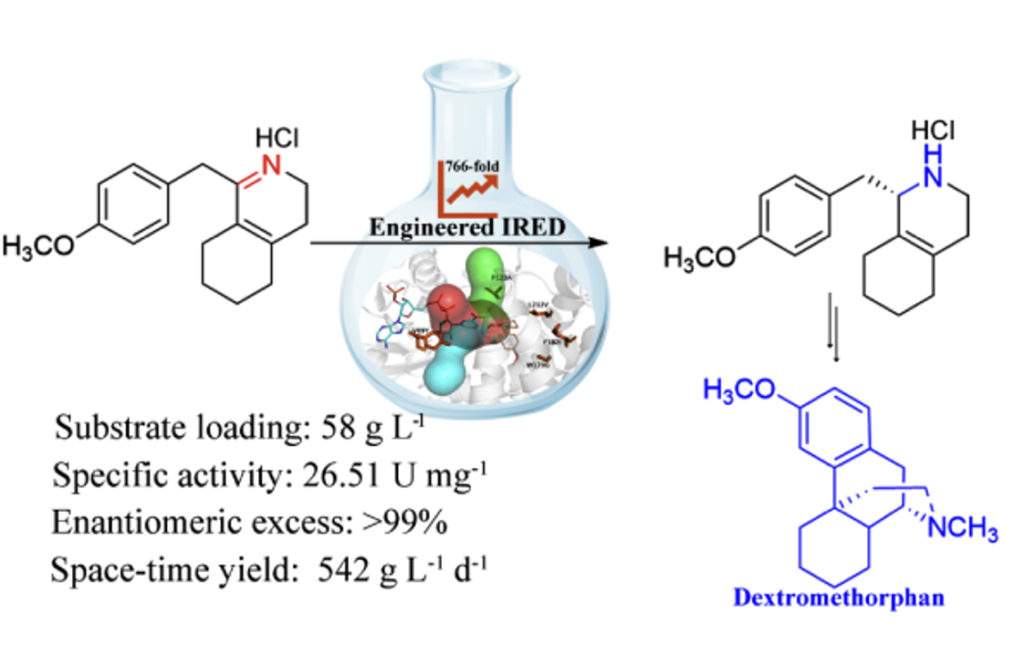
Dextromethorphan is one of the most widely used antitussive drugs. The antitussive effect of dextromethorphan is similar to that of codeine, but it is not addictive and is not prone to cause side effects such as constipation, sedation, and respiratory depression. (S)-1-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroisoquinoline ((S)-1a) is a key synthetic intermediate for the industrial production of dextromethorphan. It is mainly obtained by kinetic resolution of racemates, iridium or ruthenium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation, and deracemization of cyclohexylamine oxidase combined with boron amine, but there are problems such as low yield, low stereoselectivity, and harsh reaction conditions.
Based on the imine reductase-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of 1-benzyloctahydroisoquinoline, Zhu Dunming and Wu Qiaqing at the CAS Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology obtained five highly active mutants by screening and designing wild-type imine reductase. The enantiomeric excess of the five mutants in the catalytic synthesis of (S)-1a is >99%, the specific enzyme activity reaches 26.51 U/mg, and the catalytic efficiency is 766 times higher than that of the wild type. On this basis, the study established a laboratory-scale preparation reaction. The substrate concentration of the preparation reaction is 58 g/L, the product separation yield is 77%, and the space-time yield reaches 542 g L-1d-1, laying the foundation for further industrial application.