https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2095927323005510
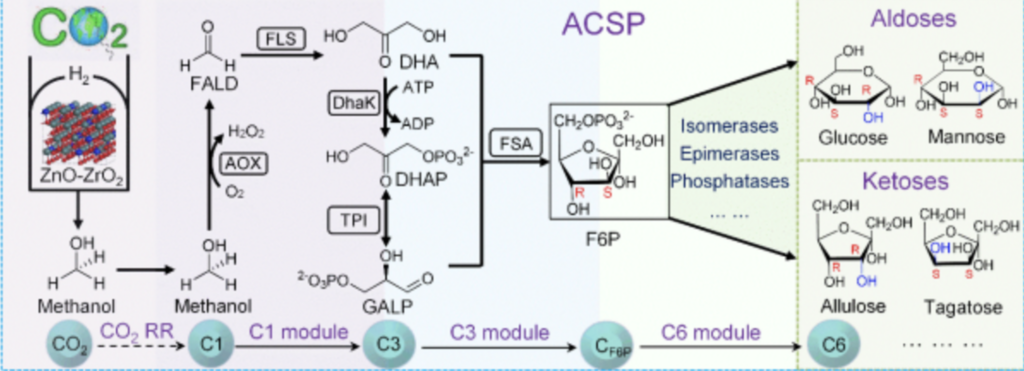
The research team of Functional Sugars and Natural Active Substances of CAS Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology has established a synthetic pathway for the synthesis of hexose from carbon dioxide in a chemical-enzymatic cascade based on the enzymatic reactions of carbon condensation, isomerization, and dephosphorylation in cooperation with CAS Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, and has improved catalytic performance of the natural enzyme activity, substrate specificity, and so on, through the enzyme molecular transformation technology. Through the enzyme molecular modification technology, the catalytic performance of the natural enzyme activity and substrate specificity were improved, and three functional modules of carbon I, carbon III, and carbon VI were constructed, and the synthesis of hexoses with different structures and functions was realized in vitro, and the conversion rate of this pathway was higher than that of traditional plant photosynthesis. At the same time, the product concentration and carbon-sugar conversion rate were higher than those of the published artificial sugar synthesis methods, such as chemical synthesis of sugar, electrochemical-yeast fermentation coupling method and other artificial sugar production methods. The sugar artificial synthesis system constructed in the study can be further coupled with other enzymatic biochemical reactions to prepare structurally diverse sugar molecules and their derivatives. Therefore, the research results establish a method to synthesize hexose from carbon monocompounds such as carbon dioxide, methanol, formaldehyde, etc., which realizes the artificial synthesis of hexose with high conversion efficiency and precise and controllable configuration, and will provide a possibility for the conversion of non-biomass raw materials to form a diversity of artificial sugar products.