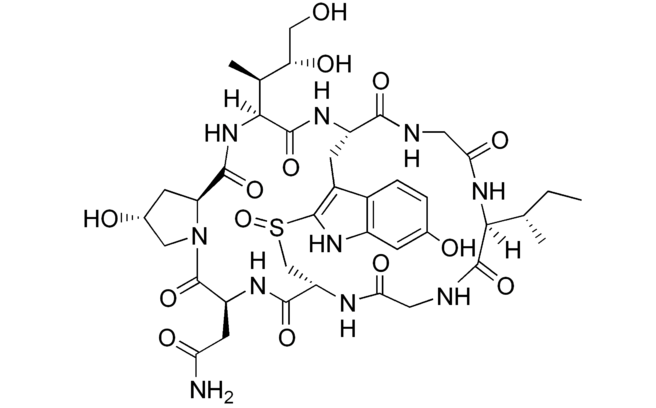
While the toxic mechanisms of poisonous mushrooms vary, mushrooms containing cyclic peptide toxin dominate. They are encoded by the “MSDIN” gene family and ribosomally biosynthesized. A typical example are the cyclic peptide toxins of Amanita mushrooms, α-amanitin and phalloidin.
In China, among the cases of mushroom poisoning deaths, 80%-90% were caused by cyclopeptide toxins. Researchers at the CAS Kunming Institute of Botany have developed a rapid detection kit for these toxins based on a reaction, under acidic conditions, with lignin to produce a blue-green complex, which can be detected already after 3 min (patent application ZL201610991804.1).
CAS news release, February 26, 2021